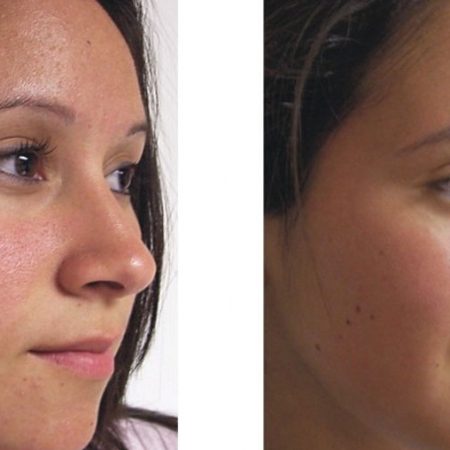
Electrolysis and Electrocoagulation
$1,320.00
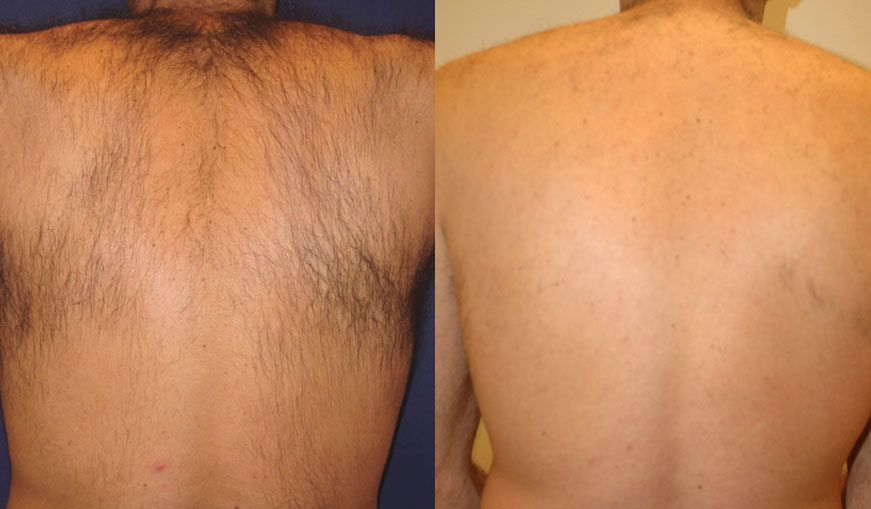
- Hair is an appendage of the skin that is slender, thread like out-growth of the skin and scalp.
- Terminal hairs are the heavier concentration of hair found on the head, under the arms, on and around the genitals and on the arms and legs.
- Vellus hair is very fine hair, or “peach fuzz” that covers most of our bodies. These hairs can be transformed into terminal hairs due to aging or increase of androgens (male hormones).
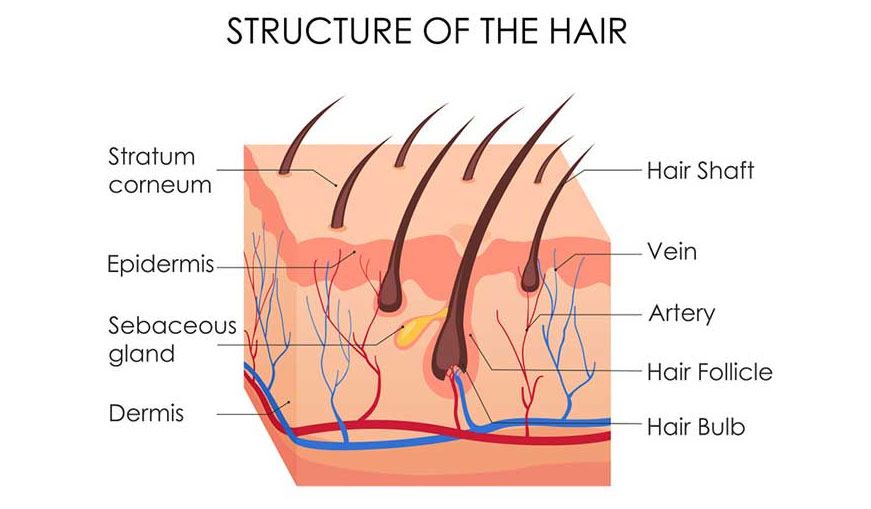
- The hair follicle begins at the bulb, which is found in the subcutaneous layer of the skin.
Hair overview (Suite)
- The bulb is surrounded by a matrix that keeps the hair follicle alive
- A thickened area of the root sheath, which lies just above the bulb, is called the bulge.
- The bulge contains stem cells that are necessary for regeneration of the hair follicle
- The bulb and the bulge are considered the “cellular center” of the hair follicle
- Melanin is concentrated in the hair shaft and upper part of the bulb, but may also be found in the bulge. This is important because melanin is the targeted chromophore which absorbs the laser light and generates heat, which in turn is conducted into the bulb and bulge.
- Remember: the goal of hair removal is to cause permanent damage to the hair follicle, including the bulb and the bulge so that it will no longer produce hairs.
Skin overview
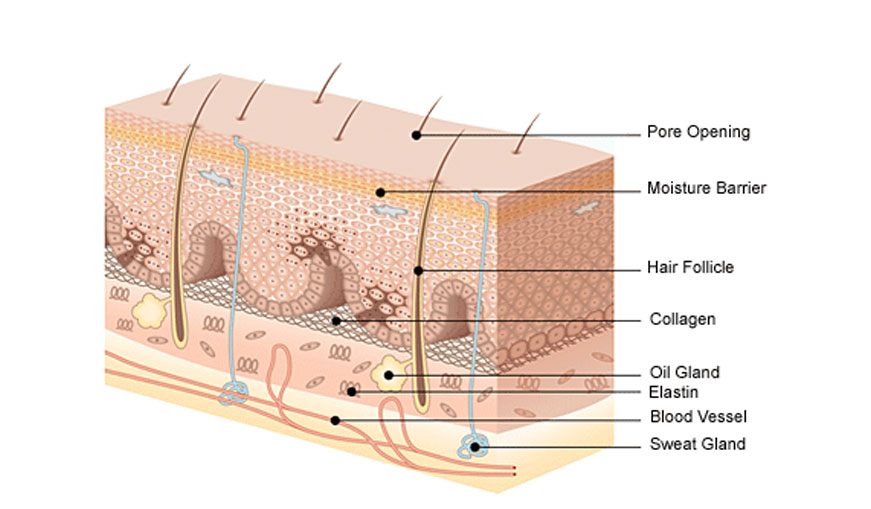
- Skin is the largest organ of the body
- Skin varies in thickness from a twelfth to a fifth of an inch (.212 cm to .508 cm)
- Skin covers at least 18.2 square feet (1.70 m2), if laid out straight end-to-end, and weights approximately 6 pounds (2.7 kg)
- Healthy skin is slightly moist, soft, flexible, possesses a slightly acid reaction and is free from disease or disorder
- Skin functions as a protective covering for the body, providing a barrier and preventing the entry of micro-organisms and harmful substances
- The epidermis is made of keratin of protein
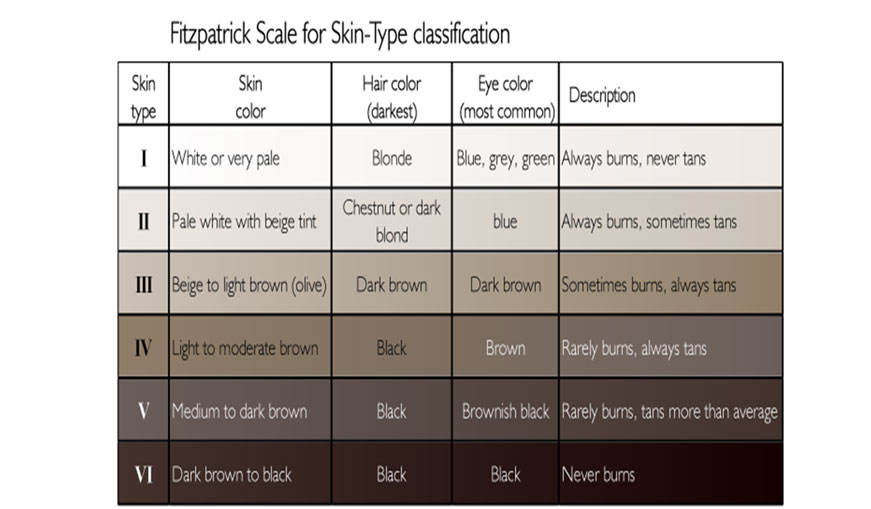
Fitzpatrick skin types scale
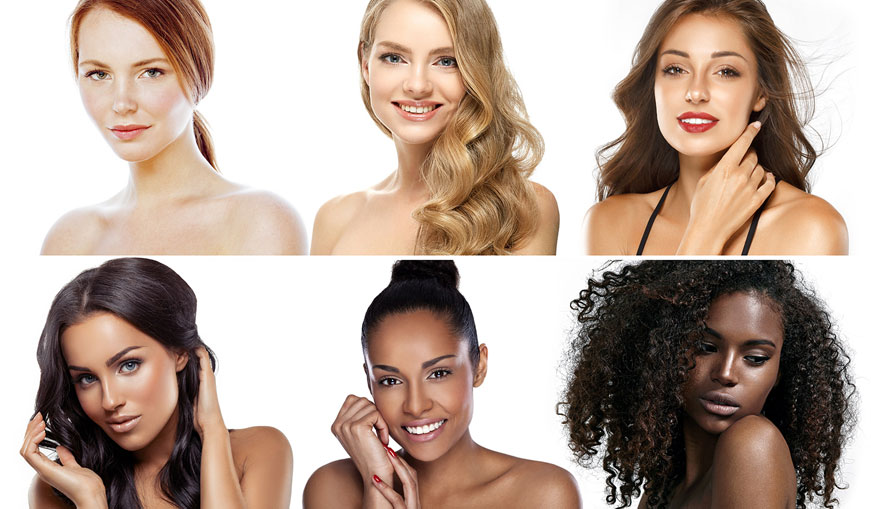

The Fitzpatrick Classification Scale was developed in 1975 by Harvard Medical School dermatologist, Thomas Fitzpatrick, MD, PhD. This scale classifies a person’s complexion and their tolerance of sunlight. It is used by many practitioners to determine how someone will respond or react to facial treatments, and how likely they are to get skin cancer.
Course Features
- Lectures 13
- Quizzes 1
- Duration 50 hours
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 0
- Assessments Yes
-
LESSON
- What is the Electrolysis?
- What areas can be treated?
- Why should I choose electrolysis over temporary methods like waxing?
- Facts about electrolysis
- How Does it Work?
- STEP BY STEP Client and Technicien Preparation
- Step By Step Contention Procedure
- Post-care indications and advises
- Electrocoagulation
- Electrocoagulation Overview
- WHAT ARE BROKEN CAPILLARIES?
- HOW DOES THE ELECTROCOAGULATION WORK?
- STEP BY STEP Procedure
- Electrolysis Exam English